Unlocking the Benefits of Epithalon for Longevity
In the quest for extended lifespan and improved health, researchers have been exploring various compounds that may hold the key to slowing down the aging process. One such compound that has garnered significant attention is Epithalon, a synthetic peptide with promising anti-aging properties. This article delves into the world of Epithalon, exploring its potential benefits, mechanisms of action, and how it can be safely used to promote longevity.
What is Epithalon and How Does It Work?
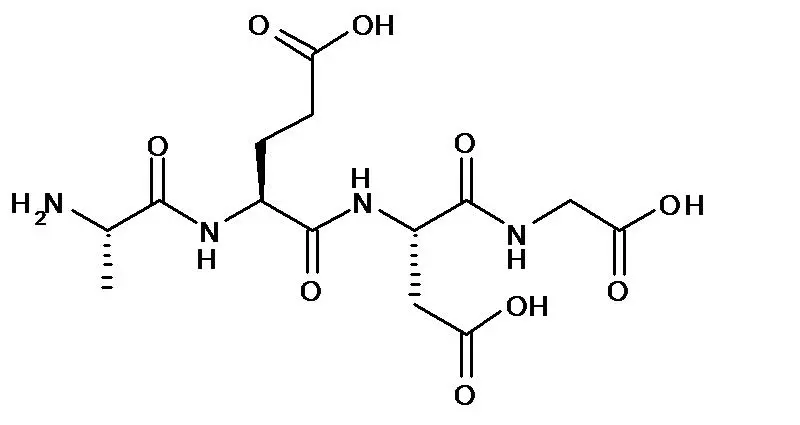
Epithalon, also known as Epitalon or Epithalamin, is a synthetic tetrapeptide composed of four amino acids: alanine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid, and glycine. It was originally developed based on studies of Epithalamin, a natural peptide produced by the pineal gland. The primary function of Epithalon is to stimulate the production of telomerase, an enzyme responsible for maintaining the length of telomeres.
Telomeres are protective structures at the ends of chromosomes that shorten with each cell division. When telomeres become critically short, cells enter a state of senescence or programmed cell death. By activating telomerase, Epithalon helps to preserve telomere length, potentially slowing down cellular aging and extending the lifespan of cells.
Moreover, Epithalon has been shown to influence the regulation of melatonin production in the pineal gland. Melatonin is a hormone crucial for maintaining circadian rhythms and has potent antioxidant properties. By modulating melatonin levels, Epithalon may contribute to improved sleep patterns and enhanced cellular protection against oxidative stress.
Top Health Benefits of Epithalon for Anti-Aging
The potential health benefits of Epithalon are numerous and varied, making it an intriguing compound in the field of anti-aging research. Here are some of the most promising benefits associated with Epithalon use:
1. Telomere Preservation
As mentioned earlier, Epithalon's ability to activate telomerase can help maintain telomere length. This preservation of telomeres may slow down cellular aging, potentially leading to increased lifespan and improved overall health.
2. Enhanced Melatonin Production
By regulating the pineal gland, Epithalon can optimize melatonin production. This can lead to improved sleep quality, better circadian rhythm regulation, and enhanced antioxidant protection for cells.
3. Improved Immune Function
Studies have suggested that Epithalon may help restore and enhance immune system function, particularly in older individuals. This could result in better resistance to infections and improved overall health.
4. Cardiovascular Health
Some research indicates that Epithalon may have cardioprotective effects, potentially reducing the risk of age-related cardiovascular diseases. It may help improve lipid profiles and reduce inflammation in the cardiovascular system.
5. Neuroprotection
Epithalon has shown promise in protecting neurons from oxidative stress and age-related damage. This neuroprotective effect could potentially help maintain cognitive function and reduce the risk of neurodegenerative disorders.
6. Antioxidant Properties
By stimulating the production of antioxidant enzymes, Epithalon may help combat oxidative stress throughout the body. This can lead to reduced cellular damage and slower aging at the molecular level.
7. Hormone Regulation
Epithalon has been observed to help regulate various hormones, including those involved in stress response and metabolism. This hormonal balancing effect may contribute to overall well-being and longevity.
8. Skin Health
Some studies suggest that Epithalon may have benefits for skin health, potentially reducing the appearance of age-related skin changes and promoting a more youthful appearance.
How to Safely Use Epithalon: Dosage and Precautions
While Epithalon shows promise in anti-aging research, it's crucial to approach its use with caution and under professional guidance. Here are some important considerations for the safe use of Epithalon:
Dosage Guidelines
The optimal dosage of Epithalon can vary depending on individual factors and specific health goals. However, common dosage protocols often involve:
- 5-10 mg per day, administered via subcutaneous injection
- Cycles of 10-20 days, followed by a break period
- Some protocols suggest using Epithalon for 1-2 cycles per year
It's important to note that these are general guidelines, and individual dosing should be determined in consultation with a healthcare professional familiar with peptide therapies.
Administration Methods
Epithalon is typically administered via subcutaneous injection. This method allows for better bioavailability compared to oral administration. Proper injection technique and sterile practices are essential to minimize the risk of infection or other complications.
Potential Side Effects
While Epithalon is generally considered to have a good safety profile, some potential side effects may include:
- Injection site reactions (redness, swelling, or itching)
- Temporary changes in sleep patterns
- Headaches
- Dizziness
These side effects are usually mild and transient. However, if any severe or persistent side effects occur, it's important to discontinue use and consult a healthcare provider.
Precautions and Contraindications
Before using Epithalon, consider the following precautions:
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: The safety of Epithalon during pregnancy or breastfeeding has not been established. It's best to avoid use during these periods.
- Medical conditions: Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions, especially hormonal disorders or cancer, should consult their healthcare provider before using Epithalon.
- Drug interactions: While specific drug interactions with Epithalon are not well-documented, it's important to inform your healthcare provider about all medications and supplements you're taking.
- Quality and sourcing: Ensure that you obtain Epithalon from reputable sources to guarantee purity and quality.
Monitoring and Follow-up
Regular health check-ups and monitoring are advisable when using Epithalon. This may include:
- Periodic blood tests to assess hormone levels and overall health markers
- Monitoring of sleep patterns and circadian rhythms
- Assessment of cognitive function and overall well-being
By closely monitoring your health and working with a knowledgeable healthcare provider, you can maximize the potential benefits of Epithalon while minimizing risks.
Conclusion
Epithalon represents an exciting frontier in anti-aging research, offering potential benefits ranging from telomere preservation to improved immune function and hormone regulation. While the compound shows promise, it's crucial to approach its use with caution and under professional guidance.
As research in this field continues to evolve, Epithalon may play an increasingly important role in strategies for promoting longevity and healthy aging. However, it's important to remember that no single compound is a magic bullet for anti-aging. A holistic approach that includes a healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management, and overall wellness practices remains the cornerstone of longevity.
If you're considering incorporating Epithalon into your anti-aging regimen, consult with a healthcare professional who specializes in peptide therapies and age management. They can help you determine if Epithalon is appropriate for your individual needs and guide you in its safe and effective use.
For more information about Epithalon and other cutting-edge anti-aging compounds, please contact us at mark@jiubaiyuanbiotech.com. Our team of experts is here to answer your questions and provide you with the highest quality products to support your longevity goals.

References
- Khavinson, V. K., & Morozov, V. G. (2003). Peptides of pineal gland and thymus prolong human life. Neuro Endocrinology Letters, 24(3-4), 233-240.
- Anisimov, V. N., et al. (2003). Effect of Epitalon on biomarkers of aging, life span and spontaneous tumor incidence in female Swiss-derived SHR mice. Biogerontology, 4(4), 193-202.
- Khavinson, V. K., et al. (2012). Peptide regulation of gene expression and protein synthesis in bronchial epithelium. Lung, 190(4), 407-411.
- Kossoy, G., et al. (2006). Effect of the synthetic pineal peptide epitalon on spontaneous carcinogenesis in female C3H/He mice. In Vivo, 20(2), 253-257.
- Khavinson, V. K., & Malinin, V. V. (2005). Gerontological aspects of genome peptide regulation. Basel: Karger Publishers.
- Anisimov, V. N., & Khavinson, V. K. (2010). Peptide bioregulation of aging: results and prospects. Biogerontology, 11(2), 139-149.
Related Industry Knowledge
- Unlocking the Benefits of Diacerein Powder for Joint Health
- The Benefits of Cassia Nomame Extract for Weight Loss
- Unlocking the Benefits of Asiaticoside 98 for Health
- Is Fusidic Acid Good For Acne?
- What Is Oleanolic Acid Used For?
- What Is Ectoin In Skincare?
- Shilajit Resin Ointment for Skincare
- What Is Ursolic Acid?
- What Makes Deoxyarbutin Powder Suitable for Sensitive Skin Types?
- Cassia Nomame Extract Benefits for Weight Loss