What Is A Cytidylic Acid?
5 Cytidylic acid, also known as cytidine monophosphate (CMP), is a nucleotide that plays a crucial role in various biological processes. It is composed of cytosine, a nitrogenous base, attached to a ribose sugar molecule and a phosphate group. CMP is involved in the synthesis of RNA and other important cellular functions. Let's delve deeper into the role and significance of 5 cytidylic acid.
In RNA synthesis, cytidylic acid participates by providing the cytosine base necessary for forming RNA molecules. This process is essential for gene expression and protein synthesis within cells. CMP is also significant in signal transduction pathways, where it regulates cellular responses to various stimuli.
Biologically, 5 Cytidylic Acid Powder contributes to the overall stability and structure of RNA molecules, influencing their function and interaction with proteins. Its presence is crucial for maintaining cellular integrity and proper metabolic functions.
What is the structure of cytidylic acid and how does it differ from other nucleotides?

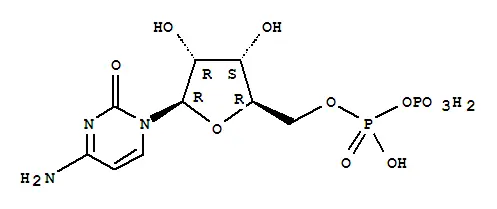
Cytidylic acid is a nucleotide, which is a structure block of nucleic acids like RNA. It comprises of three primary parts: a nitrogenous base (cytosine), a ribose sugar, and a phosphate bunch. The design of cytidylic acid is like different nucleotides, for example, adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and guanosine monophosphate (GMP), with the exception of the particular nitrogenous base joined.
Cytidylic acid, otherwise called Cytidine monophosphate powder (CMP), is a nucleotide that assumes a pivotal part in different natural cycles. Its design comprises of three fundamental parts: a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar, and a phosphate bunch.
1. Nitrogenous Base: Cytidylic acid contains a nitrogenous base called cytosine. Cytosine is one of the four standard bases tracked down in DNA and RNA. It is a pyrimidine base, described by a solitary ring structure containing carbon and nitrogen particles.
2. Five-Carbon Sugar: The sugar part in 5 Cytidylic Acid Powder is ribose. Ribose is a pentose sugar, meaning it has five carbon particles. On account of cytidylic acid, ribose shapes a glycosidic bond with the nitrogenous base cytosine.
3. Phosphate Gathering: Joined to the ribose sugar is a phosphate bunch. This phosphate bunch is significant as it permits nucleotides like cytidylic acid to connect together by means of phosphodiester bonds, framing the foundation of DNA and RNA particles.
Contrasts from Different Nucleotides:
Cytidylic acid contrasts from different nucleotides basically in its nitrogenous base:
- Adenylic Acid (AMP): Adenylic acid contains the base adenine rather than cytosine.
- Guanidylic Acid (GMP): Guanidylic acid contains the base guanine.
- Uridylic Acid (UMP): Uridylic acid contains the base uracil.
Every one of these nucleotides has an unmistakable nitrogenous base, however they all offer the normal construction of a sugar-phosphate spine. This underlying variety among nucleotides adds to the range of capabilities they act in cell processes, including energy move (ATP), protein combination (tRNA), and hereditary data stockpiling (DNA and RNA).
What are the functions of cytidylic acid in the body?
Cytidylic acid assumes a few fundamental parts in organic cycles. It is a forerunner for the combination of RNA, where it fills in as one of the structure blocks for the RNA particle. RNA is pivotal for protein amalgamation, quality guideline, and other cell capabilities. Also, 5 Cytidylic Acid Powder is engaged with lipid digestion, cell flagging, and the guideline of quality articulation.
Cytidylic acid, otherwise called Cytidine monophosphate powder (CMP), assumes a few critical parts in the body, especially inside cell processes. Here are a portion of the essential elements of cytidylic acid:
1. RNA and DNA Blend: Cytidylic acid is a nucleotide, one of the structure blocks of RNA and DNA. In RNA, cytidylic acid matches with guanine to frame the cytosine-guanine base pair, which is fundamental for the legitimate encoding of hereditary data. In DNA combination, cytidylic acid is switched over completely to deoxy Cytidine monophosphate powder (dCMP), which comparably coordinates with guanine.
2. Energy Move: Albeit not also known as adenosine triphosphate (ATP), 5 cytidylic acid is engaged with energy move inside cells. CMP can be phosphorylated to cytidine diphosphate (CDP) and cytidine triphosphate (CTP). CTP is a significant particle in energy digestion and is utilized as a substrate in different biochemical responses.
3. Phospholipid Union: Cytidylic acid is imperative for the blend of phospholipids, which are key parts of cell films. CTP consolidates with phosphatidic acid to shape CDP-diacylglycerol, which is a forerunner for the union of phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidylglycerol, and cardiolipin. These phospholipids are urgent for keeping up with cell film respectability and capability.
4. Glycoprotein and Glycolipid Blend: CMP assumes a part in the biosynthesis of glycoproteins and glycolipids, which are fundamental for cell flagging, acknowledgment, and grip. CMP-sialic acid, a subordinate of CMP, is a contributor particle in the sialylation of glycoproteins and glycolipids, impacting different natural cycles like safe reaction and cell collaborations.
5. Signal Transduction: Cytidylic acid subsidiaries are associated with signal transduction pathways. For instance, cytidine triphosphate (CTP) is utilized in the union of second couriers like cytidine diphosphate-diacylglycerol (CDP-DAG), which assume parts in communicating signals from the phone surface to the inside, hence impacting cell reactions.
6. Metabolic Intermediates: CMP and its subsidiaries act as intermediates in different metabolic pathways. They are associated with the rescue pathways of nucleotide amalgamation, which permit cells to reuse nucleotides for DNA and RNA blend effectively.
7. Cell Correspondence and Capability: As a component of nucleotides and nucleic acids, cytidylic acid is key to the capacity and articulation of hereditary data. It is likewise engaged with different cell processes including protein combination and cell correspondence.
What are the sources of cytidylic acid in the diet and are there any health benefits associated with its consumption?
5 Cytidylic acid is tracked down in different food sources, including entire grains, vegetables, nuts, and seeds. These food sources are likewise great wellsprings of different nucleotides and fundamental supplements. While cytidylic acid itself isn't normally devoured as an enhancement, a decent eating routine wealthy in food varieties containing 5 cytidylic acid can add to by and large wellbeing and prosperity. Be that as it may, more examination is expected to comprehend the particular medical advantages of cytidylic acid utilization.
1. Meat and Fish: Creature tissues are high in nucleotides, including CMP. Organ meats like liver and kidney are especially wealthy in these mixtures.
2. Fish: Fish and shellfish are phenomenal wellsprings of nucleotides. These food varieties give CMP as well as different nucleotides fundamental for different cell capabilities.
3. Dairy Items: Milk and other dairy items contain nucleotides, albeit in more modest amounts contrasted with meat and fish.
4. Yeast and Aged Food sources: Yeast removes, for example, those utilized in making specific breads and matured food varieties like lager, are wealthy in nucleotides.
5. Vegetables and Vegetables: While plant sources by and large contain lower levels of nucleotides contrasted with creature items, certain vegetables actually give a humble measure of CMP.
The medical advantages related with the utilization of cytidylic acid are connected to its job in RNA amalgamation and cell capability. Here are a portion of the potential medical advantages:
1. Worked on Mental Capability: Cytidine, the nucleoside type of CMP, is a part of phosphatidylcholine, a fundamental phospholipid in synapse layers. Sufficient degrees of cytidine can uphold cerebrum wellbeing and mental capabilities, possibly helping with memory and growing experiences.
2. Improved Safe Reaction: Nucleotides, including CMP, assume a significant part in the development and fix of cells, including resistant cells. Sufficient admission can uphold a vigorous invulnerable framework, assisting the body with battling contaminations all the more successfully.
3. Stomach Wellbeing: Nucleotides are significant for the upkeep and fix of the digestive covering. They can improve stomach wellbeing by advancing the development of advantageous stomach microbes and fixing the gastrointestinal hindrance.
4. Recuperation and Development: CMP, alongside different nucleotides, is urgent for DNA and RNA combination, which is fundamental for cell division and fix. This is especially significant for developing youngsters, competitors, and people recuperating from sickness or injury.
While cytidylic acid is a helpful part of a reasonable eating regimen, it is fundamental to consume it as a feature of a differed and nutritious eating routine to acquire the full range of its medical advantages. Extreme admission from supplements isn't by and large suggested without clinical exhortation, as a reasonable eating regimen commonly gives adequate nucleotides to solid people.
Conclusion
All in all, cytidylic acid is a significant nucleotide that assumes an essential part in different natural cycles. Its association in RNA union and other cell capabilities features its importance in keeping up with cell wellbeing and capability. Remembering food sources rich for 5 cytidylic acid in your eating routine can add to generally wellbeing and prosperity.
References:
National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 6323274, Cytidine monophosphate. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Cytidine-monophosphate (accessed on 5 June 2024).
Berg JM, Tymoczko JL, Gatto GJ. Biochemistry. 8th edition. New York: W.H. Freeman; 2015. Section 28.2, Nucleotide Biosynthesis Can Be Regulated by Feedback Inhibition.
Günther Sillero M, Gonzalo Claros M. Cytidine Triphosphate. In: Handbook of Nucleoside Synthesis. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 2002. doi:10.1002/0471221325.ch15.
Related Industry Knowledge
- What are the applications of Kanna extract to human health?
- Unlocking the Benefits of Ectoine Powder for Skin Health
- Unlocking the Benefits of Catalpol Powder for Health
- What Is Cytidine?
- What Is Pro Xylane?
- Andrographolide Powder in Traditional Medicine
- What Is Ectoin?
- Exploring the Science Behind Kaempferol Powder
- What Is Synephrine Hydrochloride?
- Benefits of Shilajit Resin Ointment